Knowledgeable SErvice Robots for Aging (KSERA)
General Information
In this international research
Leading Investigator: Prof.
Associates: N.
Feature Extraction and Learning by Hybrid Neural Ensembles for Object Recognition and Person Detection - Nils Meins
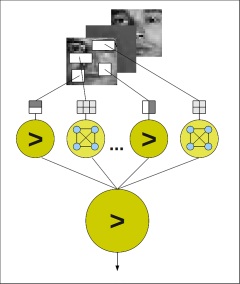
To interact with people, which are going to use the KSERA System, it is necessary for the robot to recognize a person. In order to decide whether the robot has the attention of the person, the robot has to know where the person is standing and where the person is looking to. Therefore person detection and face detection are necessary.
An ensemble is a set of classifiers that generates a classification result by querying all its members and balances the individual decisions of the classifiers. The members of the ensemble are mostly called "weak classifiers" because it is not necessary that they have good results as standalone classifiers. In this context the ensemble sometimes is called a "strong classifier". An ensemble of classifiers can mostly get better results than a single (complex) classifier. Important for the performance of an ensemble is the diversity of the classifiers that are used for the decision. Different methods exist to increase diversity of the classifiers or the underlying features. Most methods are structuring the feature-space or the training sets in some ways to focus on different aspects.
We are mostly using AdaBoost, which focuses on aspects of the training data by weighting the data points of this set, taking into account the current error of a selected classifier. We are trying to improve ensembles by using neural networks (e.g. Hopfield Neural Network) as ensemble members, but also explore to what extend they can be used as hybrid ensembles themselves in conjunction with other classification methods.
Person localization based on a ceiling-mounted camera - Wenjie Yan

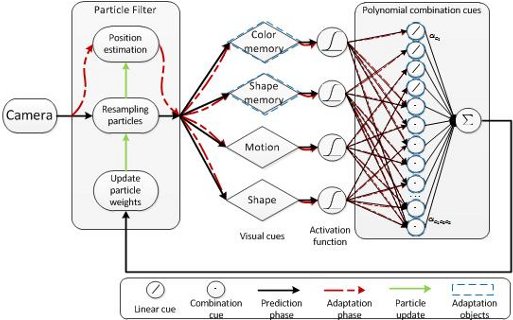
In the KSERA project we are developing a socially assistive robot that supports some activities of daily life as well as health care needs of an elderly person. A small humanoid robot Nao is the main actuator that delivers feedback from the AAL system to the person. For example, it gives health advice based on medical sensor readings and acts as a mobile communication platform for the person with remote care givers. In the absence of a care giver, the Nao robot can assist a person's life by bringing medication, providing useful information, displaying videos using a portable beamer or supporting a video communication. To achieve this, the robot must first navigate to the person's position and a robust person tracking system is therefore important.
We consider that different visual information sources can be used in combination to detect and localize a person's position reliably. A single ceiling- mounted camera with a fish-eye lens is used to keep the system simple and easy to install. A hybrid knowledge-based architecture integrates the different visual streams into a Sigma-Pi network architecture. The system is able to start localizing a person with some of the cues and acquires the other cues online for the localization. When the person is localized, the Nao robot assists by navigating to and interacting with the person.
Impressions from the Lab
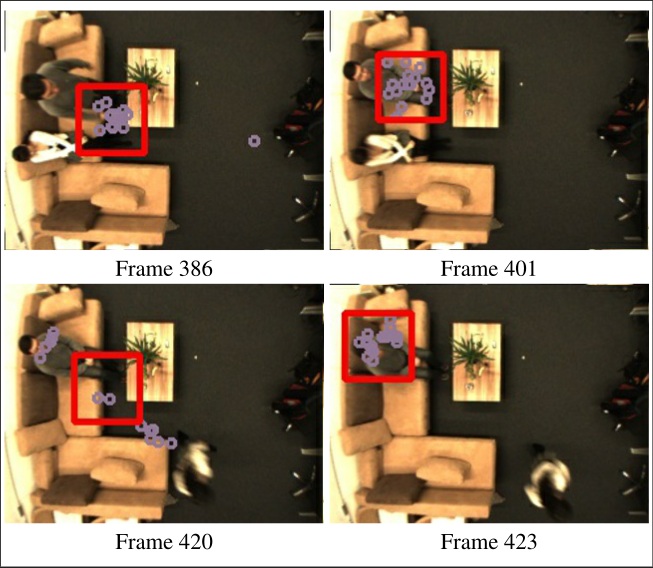 |
| The system is able to start localizing a person with some of the cues and acquires the other cues online for the localization. The reliabilities of cues, which indicate the importance of this cue for decision making, can also be adapted. A particle filter updates the person's position based on the output of this network. |
Project Publications
Further Information
The KSERA project is co-financed by the European Commission under the 7th Framework Programme (FP7) for Research and Technological Development.
